Group-4 biosynthesis
Schematic representation of Group-4 capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and surface assembly
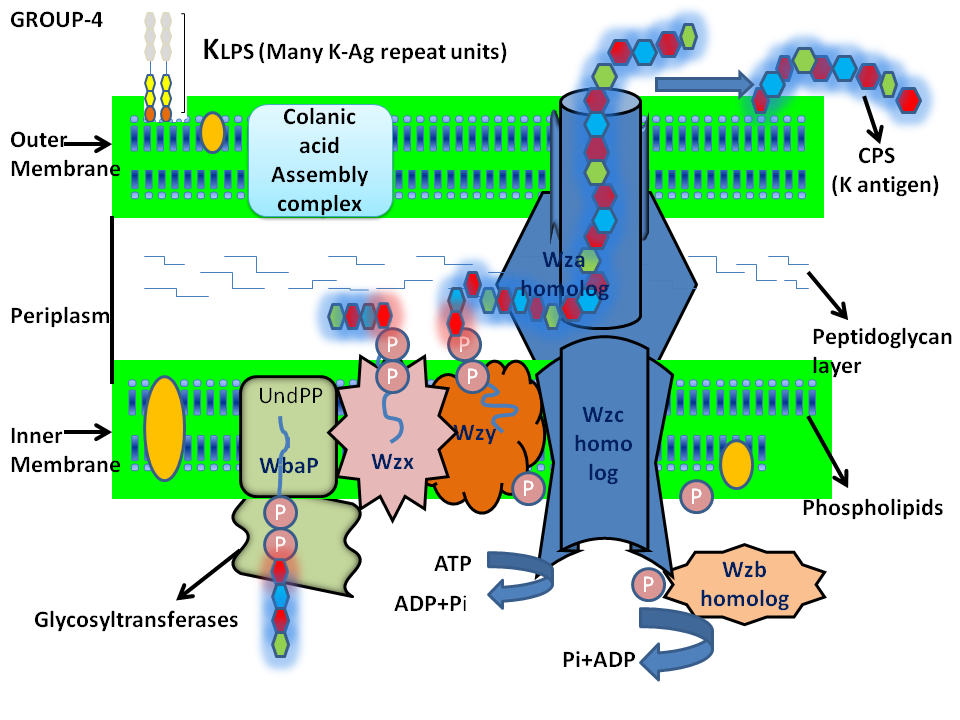
Group-4 Proteins
WecA : N-acetylhexosamine-1-phosphate transferase
GTs - 3 : Glycosyl transferase
Wzx : Repeat unit exporter ( Flippase)
Wzy : Repeat unit polymerase
Wza : Putative outer membrane lectin (Translocon)
Wzb/Etp : Putative acid phosphatase
Wzc/Etk : Putative trans membrane protein (Autokinase)
- Group-1 KLPS has few K-antigen repeats and group 4 has long chains of K antigen repeat units. Some isolates are given O-antigen status (examples include O26, O55, O100, O111, O113, and O127) and others have K-antigen status (e.g., K40) because they (like group 1 K antigens) are found in isolates that co express an additional neutral O antigen (i.e., one of O8, O9, O9a, O20, and O101 group)
- The distribution between the capsular and KLPS forms point to complex interplay in surface polymers that may be critical in understanding the pathogenicity.
Regulation of Colanic Acid production
- In contrast to the serotype-specific group 1 capsules, an exopolysaccharide is colonic acid produced upon active transcription of cps locus
- The genes are regulated based on altered conditions like osmotic shock, damaged cell envelope structure etc. Colanic acid helps to withstand dessication, by forming biofilms. But, they don't have a role in virulence.
- The location of this locus is upstream of galF in group 2, 3, 4 capsules and E.coli K12 isolates
- The colanic acid locus is similar to group-1 locus with homologs wza, wzb and wzc (wzi absent) at 5' end. Stem loop transcriptional attenuator separates wzx and (biosynthetic region) from region1.
- The Rcs system plays a major role in controlling the regulation of colanic acid transcription. It is a complex phosphorelay system that encodes for proteins involved in capsular synthesis.
- Due to genetic rearrangement in these regions colanic acid genes are absent incase of group1(Whitfield et al., 2006)