Group-2 biosynthesis
Schematic representation of Group-2 capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and surface assembly
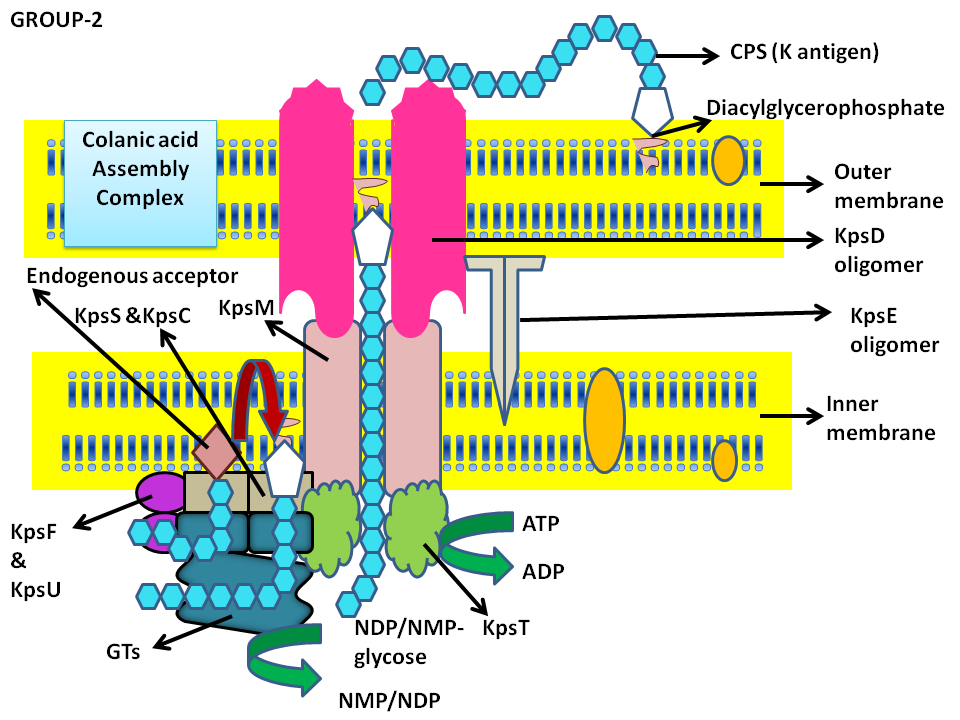
Group-2 Proteins
WbaP : Initial Glycosyl transferase
Wzz : Chain length dictator
WaaL : Polymerization terminator
GTs : Glycosyl transferase
KpsMT : ABC transporters
KpsE :Adaptor protein
KpsD :Outer membrane translocon
- The group 2 and 3 biosynthesis occurs at kps loci near ser A and involves many conserved proteins. The genetic organization and regulatory features differ. The chromosomal loci for group-2 has 3 regions (Barrett B, Ebah L, Roberts IS, 2002). Region-1 encodes for proteins involved in export and assembly of capular polysaccharide. Region 2 is centrally located and serotype specific and codes for the GTs and specialized nucleotide sugar synthetases. Region 3 encodes ABC transporter that is involved in polymer export across the inner membrane.
- Six proteins are encoded by region1(kps FEDUCS). Region 2 encodes Neu enzymes and region 3 encodes gene products kps MT. Region 1 and 3 promoters are transcriptionally silent at 20◦C temperature and this is defining feature of group-2 organisms (Thermoregulatory property) (Rowe S, et al., 2000).
- The best charecterized GTs in K1 and K92 are polysialyltransferases. NeuS transfers Neu5Ac residues from CMP-Neu5Ac to the nonreducing terminus of the nascent glycan. The poly-α-2,8-sialyltransferase (NeuS) from K1 and K92 NeuS homolog that generates a polymer with alternating α- 2,8/α-2,9 linkages in serotype indicates NeuS enzymes are the sole determinants of serotype specificity, and the K92 NeuS enzyme has dual linkage specificity.
- ABC transporters help in transport of capsular polysaccharide incase of group-2. The polymer formation is initiated on the endogenous acceptor and elongation occurs at the non reducing terminus of the chain with the involvement of GTs. Kdo(Diacyl glycero phosphate) is known to be linked to the polymer and is exported with the help of KpsM and KpsT proteins (Inner membrane) of the ABC transporter system. The proteins KpsF, KpsU, KpsS, KpsC are known to be essential for transport. KpsE and KpsD are involved in transloaction process (Whitefield 2006).
- In E.coli K1 maximum chain length 160-230 residues. No obvious enzymes are involved in this process. However, abortive chain translocation process within the catalytic site (loss of GTs affinity for polymer) or an allosteric effect by other components involved in assembly leads to termination.