Documentation
The following documentation is to help the user in usage of K-PAM web server. K-PAM web server has three major modules: (i) serotype prediction (K-type and O-type), (ii) 3-diemsional structural depository of surface antigens (75 K-antigens and 11 O-antigen associated LPS) and (iii) K-antigen modeler, and an additional module (iv) hypervirulent strain identifiction. All the modules are described in detail under individual sections.
Construction of local database
A local database comprising of Klebsiella spp. wza,wzb,wzc,wzi,wzx,wzy,wbap and wcaj gene as well as their protein sequences (whose K-types are already known) has been constructed by fetching the FASTA format sequences from NCBI or Kaptive web server and are grouped according to 141 distinct K-serotypes. It is noteworthy that the newly defined K-types, namely KN1-KN3, KL103-KL128, KL130-KL153, KL155 and KL157-KL165, whose phenotype is not yet defined, has also been incorporated in the database. Thus, the database consists of 1345 and 1095 non-redundant gene and protein sequences respectively corresponding to 8 genes in the CPS-loci.
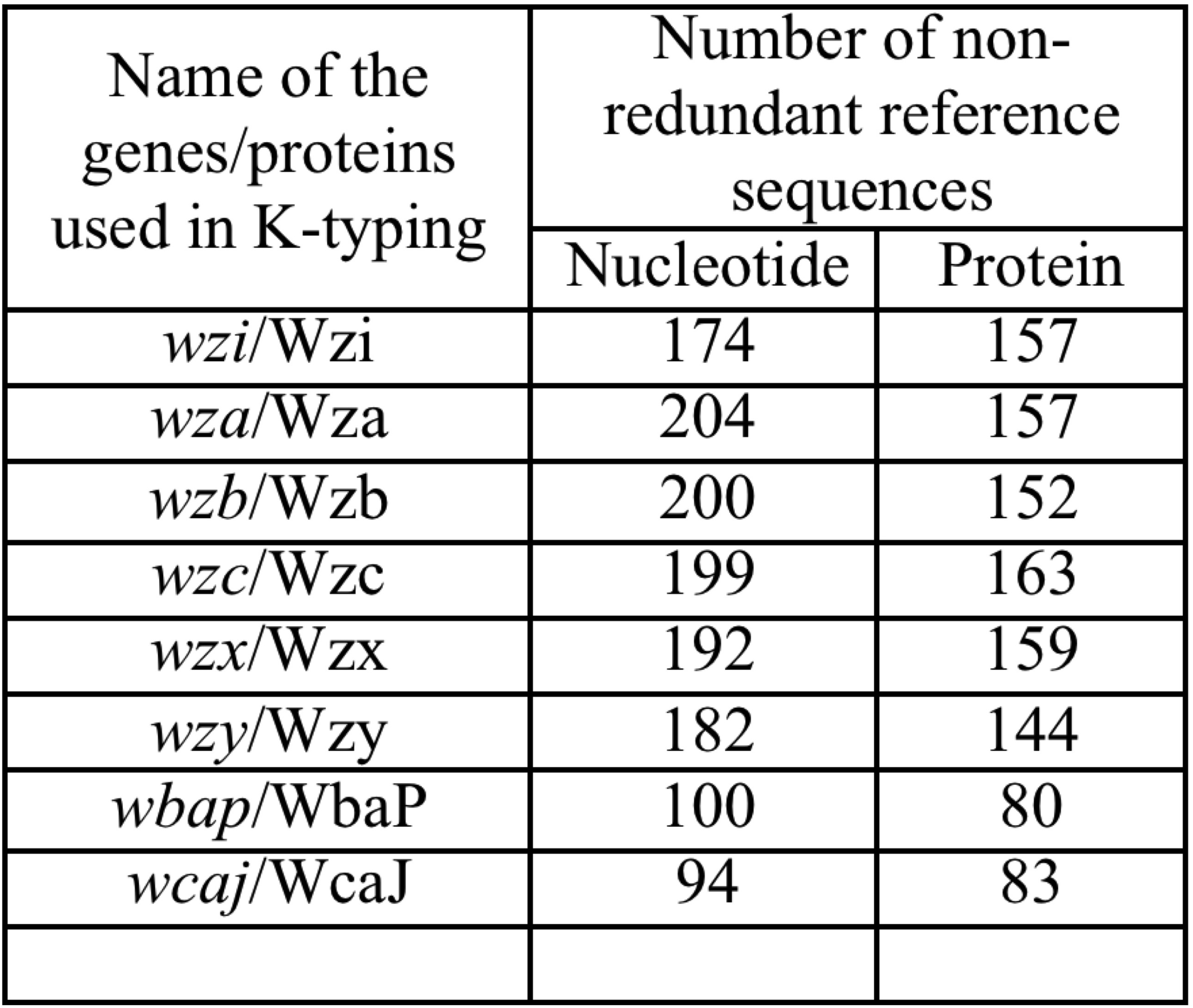
The genes that lack the sequence corresponding to a particular K-type (given in the bracket) are: wzi (K33 & K40), wzb (K50), wzc (K50), wzx (K34, K50, KL107 & KL127) and wzy (K29, K50, K71, KL107, KL108, KL109, KL110, KL113, KL116, KL118, KL126, KL147, KL148, KL149, KL150, KL152, KL153, KL157, KL158 & KL161). Note that wbap & wcaj are mutually exclusive genes.
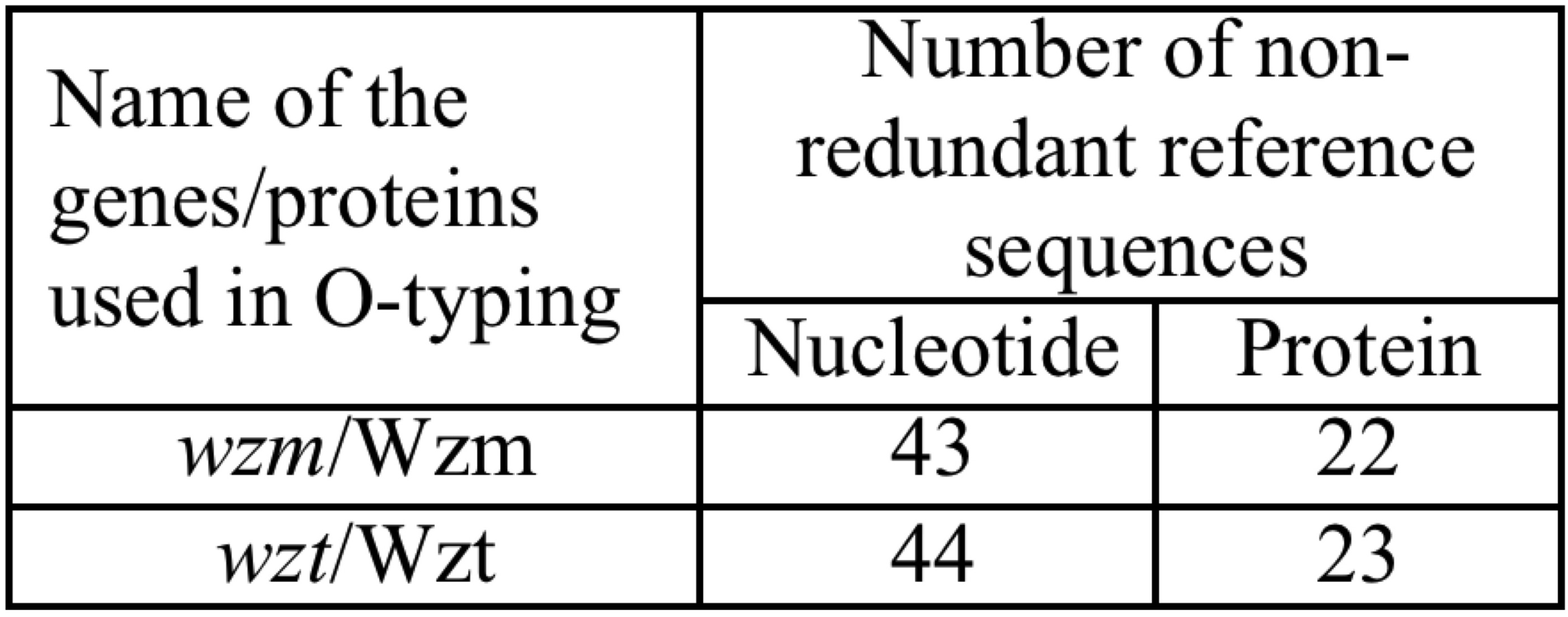
Similarly, the database also has a total of 13 distinct O-antigen serotypes including 4 sequences that belong to Klebsiella O-antigen types OL101-OL104. Further, to perform O-antigen prediction, 43 wzm and 44 wzt gene sequences and 22 Wzm and 23 Wzt protein sequences that are classified according to their O-antigen type have been incorporated in the database.
Complete list of Genbank accession numbers corresponding to CPS locus genes and wzm & wzt are provided here:
K-antigen typing
K-PAM provides the freedom of using a single or multiple genes for K-typing. The user can either specify the gene type or let the server to identify it. Thus, either a single gene or entire CPS locus or whole genome sequence can be given as input for prediction. Gene or protein sequences (FASTA format) corresponding to one or more CPS genes (wza, wzb, wzc, wzi, wzx, wzy, wbap and wcaj) can be used as input for K-type prediction. The user can also upload the whole genome sequence in either FASTA or FASTQ format as single or multiple files. Additionally, the user has the option of directly specifying the GenBank ID. K-PAM offers three options for the users to perform K-type prediction under single or multiple gene options: a) nucleotide sequence searched against nucleotide sequence in the reference database (NN), b) protein sequence searched against protein sequence reference database (PP) and c) nucleotide sequence searched against protein sequence in the reference database (NP).
Input for K-antigen typing
Query sequence information can be given to the server as any of the following ways:
- NCBI Genbank ID (nucleotide ID or protein ID) associated with the sequence
- Through manual entry of nucleotide or protein sequence in fasta format
- Upload the file containing the query sequence
- Multiple files as query (For standalone version)
Sample input sequences for manual entry
- Nucleotide input query sequence with multiple coding regions or as a complete fasta sequence (input for NN/NP options): sample_nn.fasta (OR) sample_nn_unannotated.fasta
- Protein input query sequence with multiple coding regions (Input for PP option): sample_pp.fasta
Note: If genomic DNA and plasmid DNA sequences of a strain are stored in a single file, use the stand-alone version of K-PAM for serotype prediction, else store the sequences in individual files before submitting to web-gui of K-PAM.
Sample example for filling form for serotyping with single gene sequence or with query sequence containing multiple coding regions in the Serotype predictor subpage is given below.
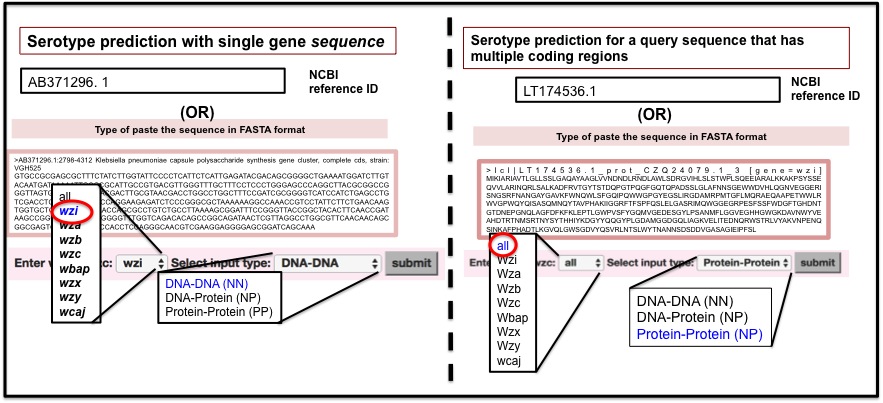
Output for K-antigen typing with single gene query
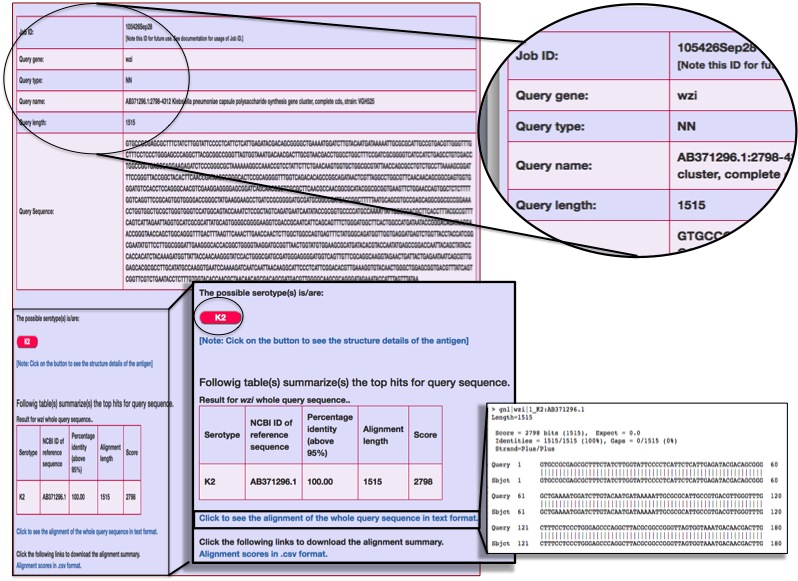
Some test cases corresponding to the clinically important Klebsiella species whose serotypes are undefined are used to demonstrate the serotype prediction method using single protein coding region. The output are listed in the file : Table_single_prot.pdf
Use of more than one protein coding region increased the prediction accuracy
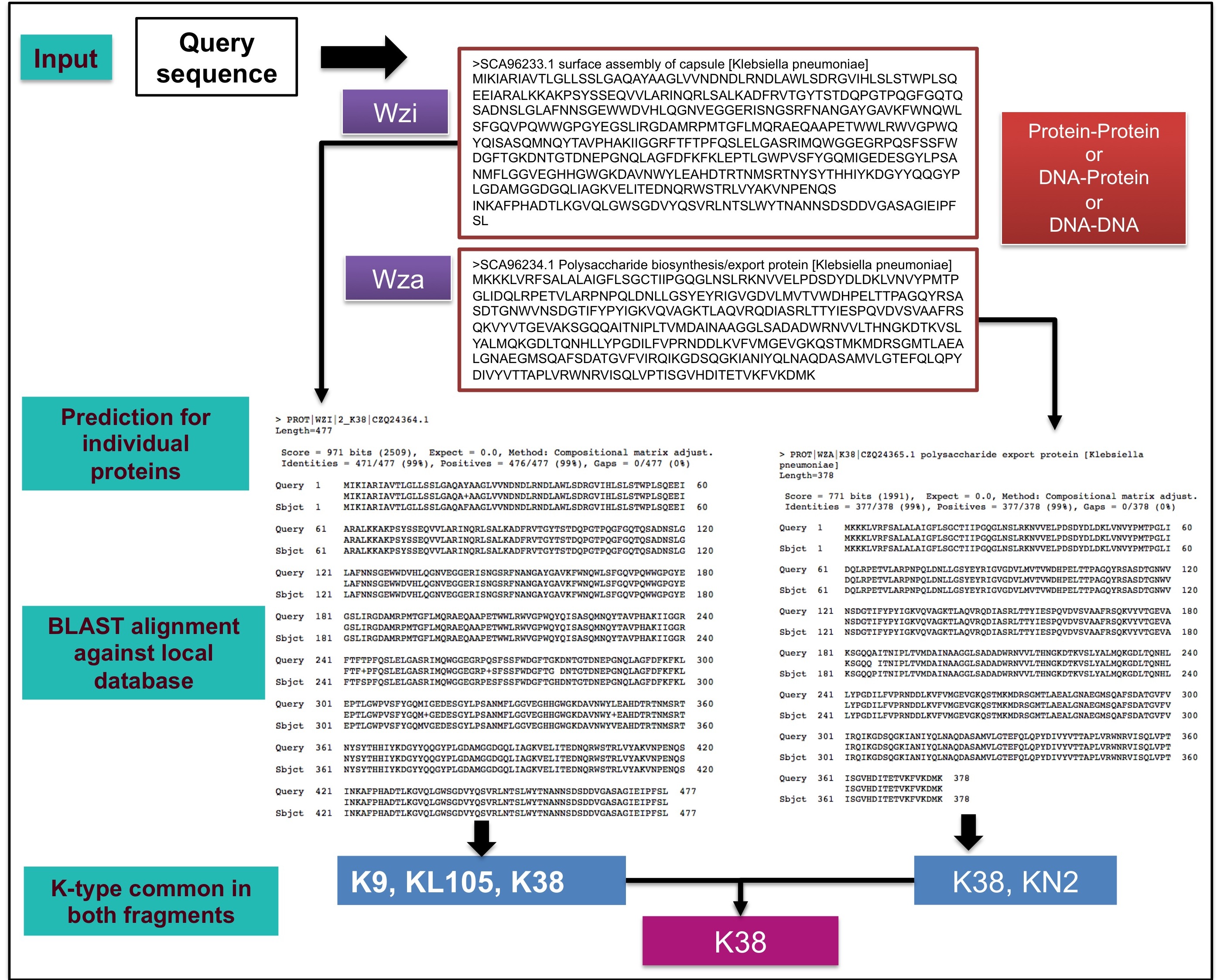
The figure above is a schematic illustration of K-typing using both Wzi & Wza. Protein query sequences corresponding to both Wzi and Wza (NCBI accession ID: SCA96233.1 and SCA96234.1 respectively) are aligned against the respective reference sequences stored in the local database. The common outcome from both the alignments is considered as the predicted K-type for the input query sequences.
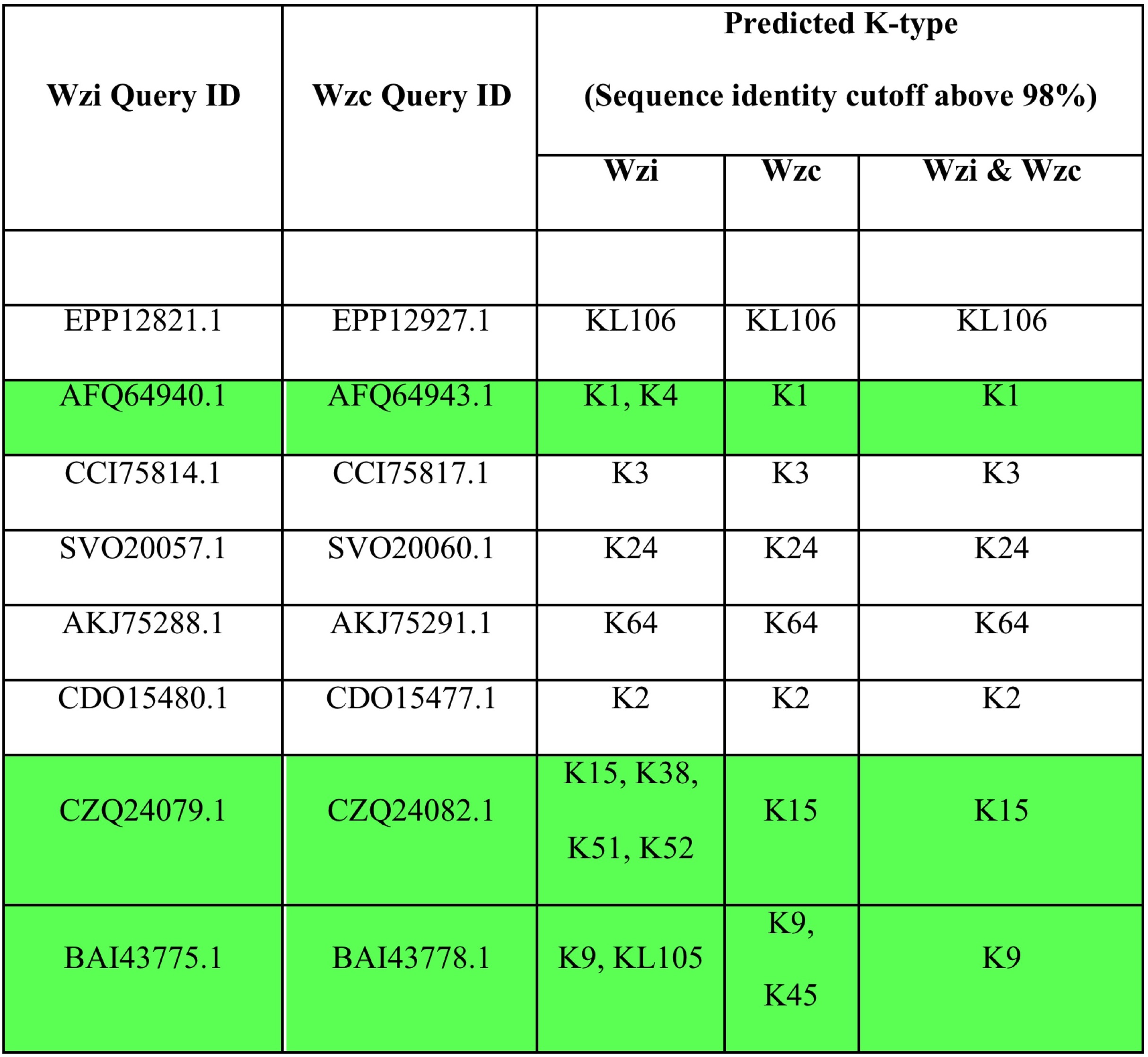
Few similar examples illustrating the importance of K-type prediction by the combined use of Wzi and Wzc sequences (highlighted in green) has been shown in the table below.
Use of only eight cps protein coding regions in K-typing
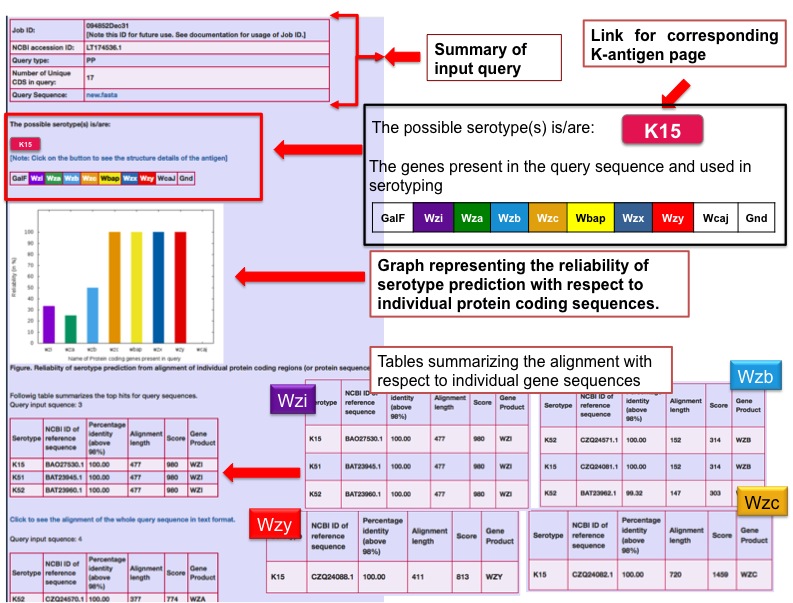
Output for K-antigen typing with a query sequence with multiple coding regionsThe serotype prediction example considering multiple protein coding regions in the query sequence (NCBI accession number LT174536.1). An input box is provided for submitting either an NCBI accession ID or a query sequence along with the options to choose the gene/protein type (or “all”, if gene information is unknown) and the type of alignment (NN, PP or NP). The predicted serotype is shown (here, K15) in the result page. The proteins present in the query sequence and used in serotyping are given in the color-coded box. The user can get the antigen structural/chemical details by clicking the serotype button. A graph representing the reliability of serotype prediction with respect to the individual protein coding sequences. D) Tables (stacked) summarizing the prediction with respect to the individual gene sequences.
Sample examples for serotyping with single gene sequences and different modes of input are provided in the Serotype predictor subpage is given below.
K-PAM also has the feature to distinguish the hyper virulent Klebsiella spp form the classical klebsiella spp using five genes, rmpA, rmpA2, iucA, iroB, and peg-344 which are reported as efficient hyper virulent klebsiella strain markers in the earlier investigations (Russo et. al., 2018). It is worth noting that iroB, iucA, rmpA & rmpA2 and peg-344 genes correspond to the loci of salmochelin siderophore, aerobactin siderophore, hypermucoidy and putative transportation respectively (Ruso et. al., 2018 and Russo and Marr, 2019). The reference dataset of K-PAM has these gene sequences and a sequence identity cutoff criterion of 60% is used to identify the presence of these genes in the query sequence.
Submit your query sequence in "Hypervirulent identification" subpage.
A standalone version (application program interface (API)) of K-PAM is also available for analyzing the large datasets. It has the option to upload multiple files. The executable files correspond to Mac, Linux and Windows operating system can be downloaded from the API subpage . This standalone version has the K-typing, O-typing and hypervirulent strain identification features. The K-PAM API generates the serotype prediction summary in the CSV file format. The other details related to usage of API is given in the API subpage.
In addition to the serotype prediction, the server also has the database of the modeled 3D structures of 75 K- and 11 O-antigens.
Nomenclature used in chemical representation of monosaccharides in K-PAM
Sugar name: α-L-Fucp
Position: 1-2-3456
1: α and β represent the anomeric forms of the sugar molecules
2: D and L represent the enantiomers of the sugar molecule
345: Tri-letter sugar code (see below)
6: The molecule name terminates with’ p’ or ‘f’ is for pyranose or furanose sugar forms respectively
Fuc=Fucose
Gal=Galactose
Glc=Glucose
Rha=Rhamnose
Man=Mannose
GalpA=Galacturonic acid (Pyranose)
GlcpA=Glucoronic acid (Pyranose)
GlcNAc = N Acetyl Glucosamine
Ribf= Ribofuranose
Oac= O-acetyl group
Pyr= pyruvyl group
β-L-Sug= 4-deoxy-three-hex-4-enopyranosyluronic acid
Glu=Glutamate
For=Formate
Olac= Acetylated lactic acid derivative
Schematic representation
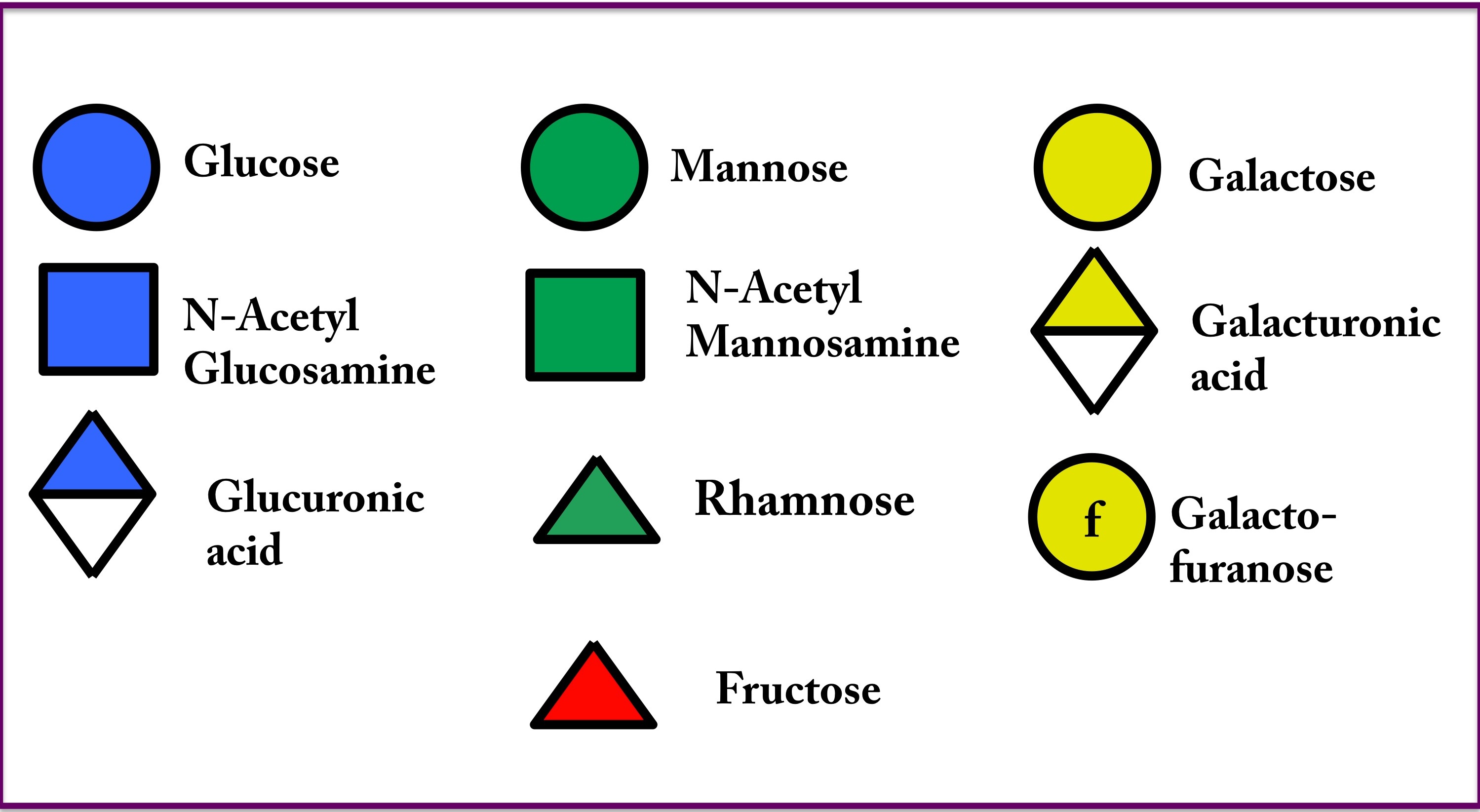
The schematic representation has been adopted from the glycan representation developed by the Consortium for functional glycomics (CFG) for sugars without derivatives and for sugars with derivatives, the representations are modified.
Antigen modeling Methodology
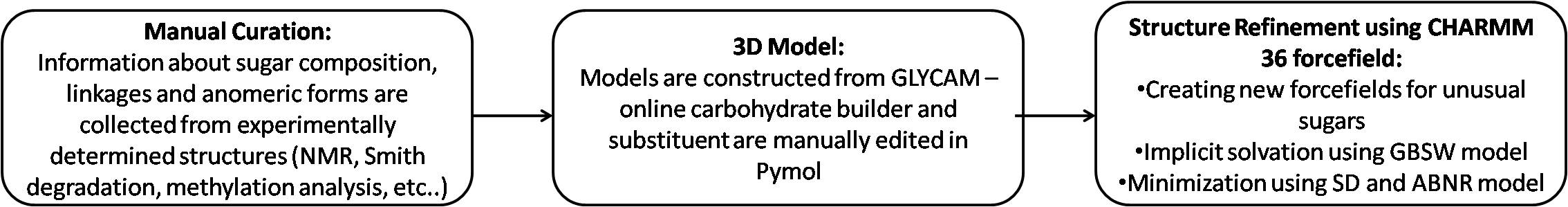
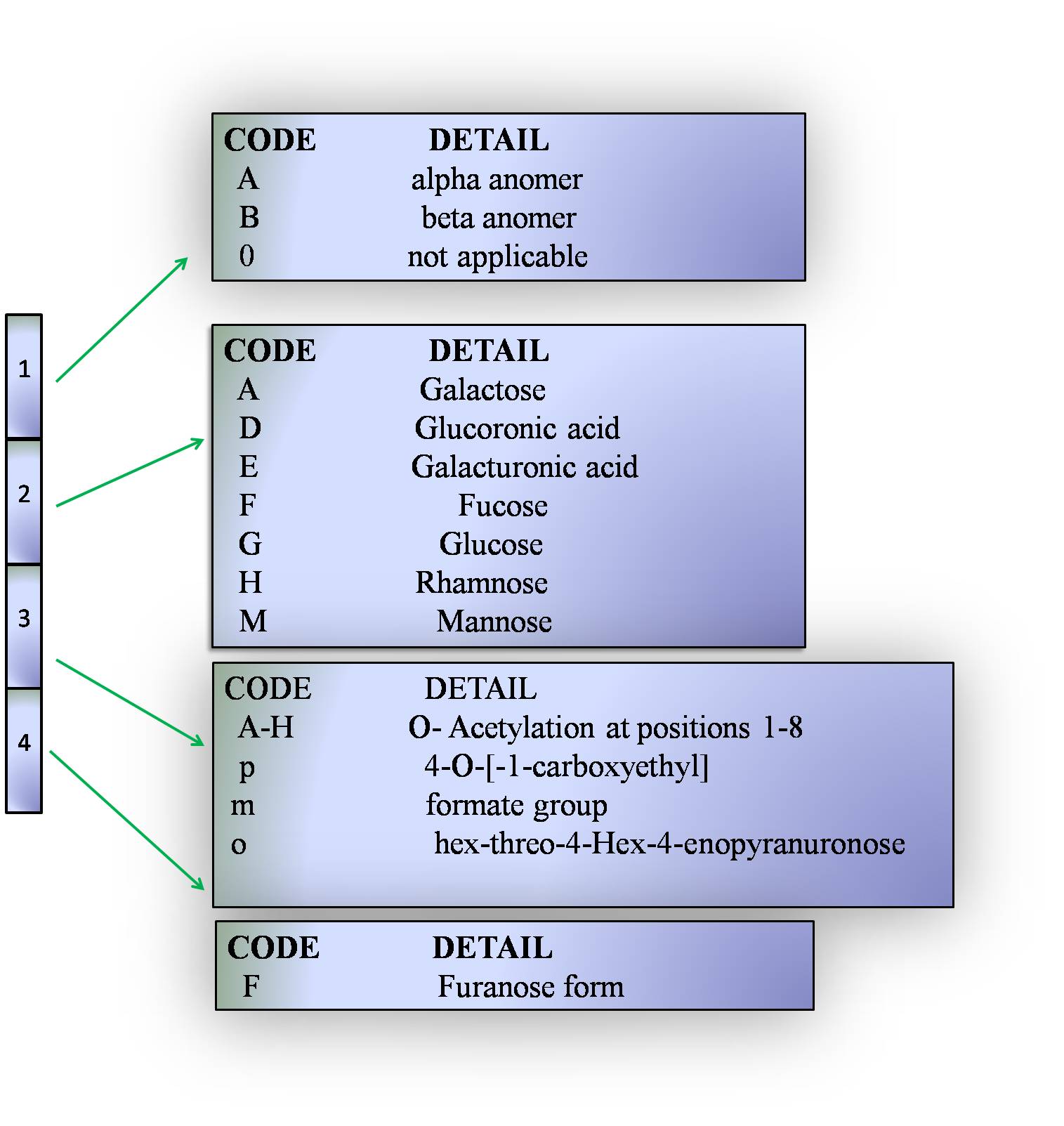
Four letter code
The following explains the four letter code for the carbohydrates used in K-PAM
The four letter code for the carbohydrates used in K-PAM